WAVES
Freepik | digital art
In physics, a wave is a disturbance that regularly moves from one location to another. Simple waves have a set frequency (the number of waves that pass a certain point over one second) and wavelength (the length of the repeated section of the wave).
Sound is an example of a mechanical wave, or one that requires a medium to travel through. All phases of matter can transmit sound in longitudinal waves — waves where the disturbance is in the same direction as the wave). In solids, sound can also be transmitted as a transverse wave — waves whose disturbance is perpendicular to the direction of the wave. Most waves in nature, including sound, are sine waves, which (unsurprisingly) are waves that move in the shape of a sine function.
Sound Waves
Freepik | digital art
Sysco. co | digital art
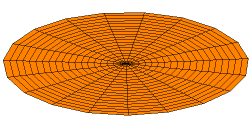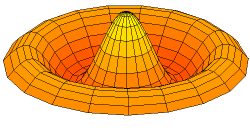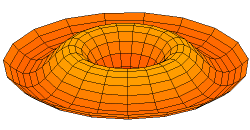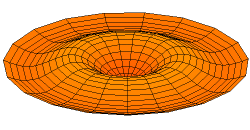
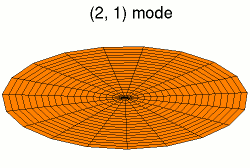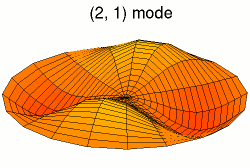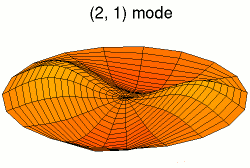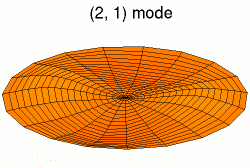
A normal mode is a motion pattern where the system moves sinusoidally at the same frequency and a fixed phase relation. The frequency of a normal mode is called a natural or resonant frequency.
The superposition principle describes how when more than one stimulus is present, the response of the surface will be the sum of the responses for each individual stimulus. The most general motion pattern that a surface follows is the superposition of its normal modes.
Models are in the public domain
Cymatics
Hans Jenny, a Swiss physician and natural scientist, coined the term cymatics in 1967. More scientifically, cymatics is a type of modal vibration — in other words, a motion pattern where the system moves sinusoidally (in the shape of a sine function).
One way to visualize sound is to sprinkle fine particles like dust or flour on a membrane. Playing a sound, which moves the membrane, will cause the particles to move according to the vibrations, creating intricate patterns.
the science of visualizing sound
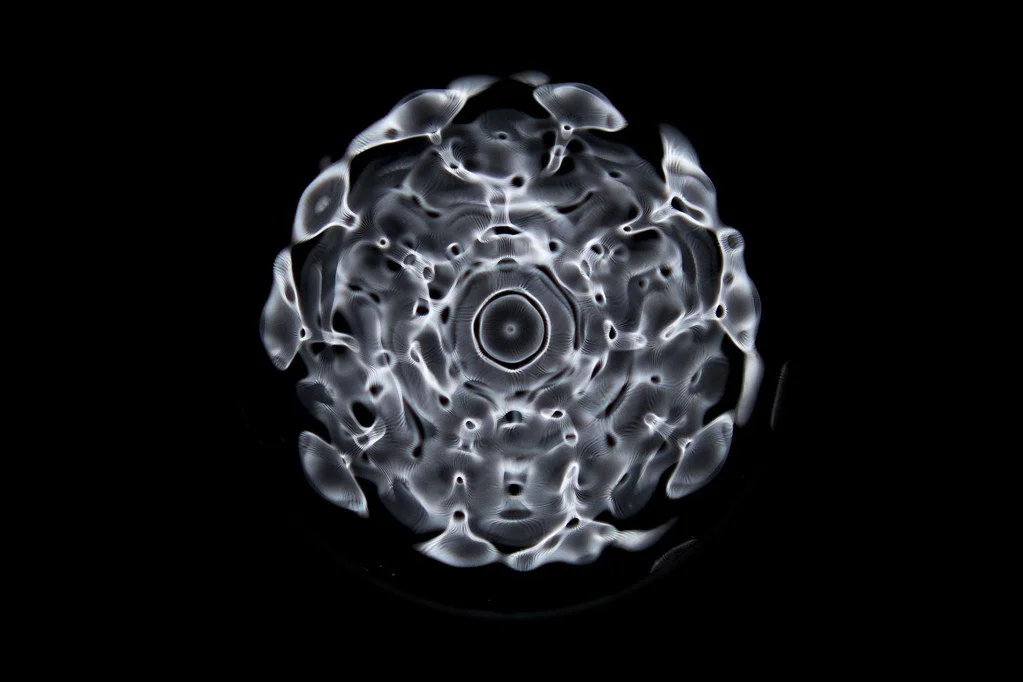









Above images from Flickr | photography
Web Page Design by ASHLEY HU and JOYCE MA